Integrative Biomedical Research
Predictive Angiogenesis-Cancer-Artificial Intelligence (PA-C-AI): Advancing Precision Medicine through Machine Learning for Personalized Treatment
S. Ariffa Begum1*, J. Raja2, N. Srinivas3, R. Nagendran4, G. Umamaheswari5, Srithar S6
Journal of Angiotherapy 8 (11) 1-12 https://doi.org/10.25163/angiotherapy.81110018
Submitted: 19 August 2024 Revised: 02 November 2024 Published: 03 November 2024
Abstract
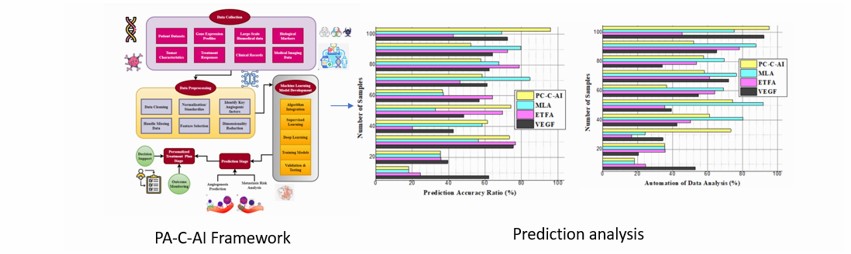
Background: Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, plays a critical role in cancer progression and other pathological conditions such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetic retinopathy. Predicting angiogenic patterns with high precision is vital for personalizing treatment and improving patient outcomes. The Predictive Angiogenesis-Cancer-Artificial Intelligence (PA-C-AI) framework combines artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to address limitations in traditional methods, such as dependency on human expertise and limited data scalability. Methods: The PA-C-AI system integrates advanced machine learning algorithms, including neural networks, to analyze complex biological datasets. Multi-omics data and real-time patient monitoring were incorporated to enhance the system's accuracy and flexibility. A diverse dataset of angiogenesis markers was used to train and validate the framework. Automated data analysis eliminated bias, ensuring consistent and reproducible results. Results: The PA-C-AI framework achieved 96.2% prediction accuracy in modeling angiogenesis, significantly surpassing traditional approaches. It effectively distinguished angiogenic mechanisms, including sprouting, intussusceptive angiogenesis, and vascular mimicry, addressing gaps in current research. Personalized treatment plans demonstrated a 97.2% success rate, with improved therapeutic outcomes reported at 99.3%. The automated processes achieved 95.38% efficiency in data interpretation. Conclusion: The PA-C-AI system represents a transformative step forward in precision medicine, offering enhanced prediction of angiogenesis, personalized treatment planning, and interdisciplinary collaboration. Its applications extend beyond cancer to other angiogenesis-dependent diseases, such as cardiovascular conditions and diabetic retinopathy. Future developments will focus on expanding prediction capabilities and validating the system's clinical significance to facilitate integration into healthcare systems for AI-enhanced, patient-specific therapies.
Keywords: Angiogenesis, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Personalized Medicine, Cancer Therapy
References
Agboklu, M., Adrah, F. A., Agbenyo, P. M., & Nyavor, H. (2024). From bits to atoms: Machine learning and nanotechnology for cancer therapy. Journal of Nanotechnology Research, 6(1), 16-26. https://doi.org/ 10.26502/ jnr.2688-85210042
Aslam, M. S., & Ahmad, M. A. (Eds.). (2023). Multidisciplinary Applications of Natural Science for Drug Discovery and Integrative Medicine. IGI Global.
Baranzini, S., Börner, K., Morris, J., Nelson, C., Soman, K., Schleimer, E., ... & Huang, S. (2022). A biomedical open knowledge network harnesses the power of AI to understand deep human biology. AI magazine, 43(1), 46-58. https://doi.org/10.1002/aaai.12037
Beyer, T., Bailey, D. L., Birk, U. J., Buvat, I., Catana, C., Cheng, Z., ... & Moser, E. (2021). Medical Physics and imaging–A timely perspective. Frontiers in Physics, 9, 634693. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2021.634693
Bouten, C. V., Cheng, C., Vermue, I. M., Gawlitta, D., & Passier, R. (2022). Cardiovascular tissue engineering and regeneration: a plead for further knowledge convergence. Tissue Engineering Part A, 28(11-12), 525-541. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2021.0231
Carpentier, G., Berndt, S., Ferratge, S., Rasband, W., Cuendet, M., Uzan, G., & Albanese, P. (2020). Angiogenesis analyzer for ImageJ—A comparative morphometric analysis of “endothelial tube formation assay” and “fibrin bead assay”. Scientific reports, 10(1), 11568. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67289-8
Chen, L., Wang, W., Bai, Z., Xu, P., Fang, Y., Fang, J., ... & Tu, C. (2024). PharmaGPT: Domain-Specific Large Language Models for Bio-Pharmaceutical and Chemistry. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.18045. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.18045
Eelen, G., Treps, L., Li, X., & Carmeliet, P. (2020). Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis updated. Circulation research, 127(2), 310-329. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316851
Eftimie, R., Mavrodin, A., & Bordas, S. P. (2023). From digital control to digital twins in medicine: A brief review and future perspectives. Advances in Applied Mechanics, 56, 323-368. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aams.2022.09.001
Gholap, A. D., Uddin, M. J., Faiyazuddin, M., Omri, A., Gowri, S., & Khalid, M. (2024). Advances in Artificial Intelligence in Drug Delivery and Development: A Comprehensive Review. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 108702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108702
Kang, Z., Dou, Q., Huang, T., Tu, M., Zhong, Y., Wang, M., & Li, T. (2022). An angiogenesis-related lncRNA signature for the prognostic prediction of patients with bladder cancer and LINC02321 promotes bladder cancer progression via the VEGFA signaling pathway. Molecular Medicine Reports, 27(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2022.12925
Khansari, N. (2024). AI machine learning improves personalized cancer therapies. Australasian Medical Journal (Online), 17(2), 1166-1173. https://doi.org/10.21767/AMJ.2024.4019
Kiessling, F., & Schulz, V. (2022, July). Perspectives of Evidence-Based Therapy Management. In RöFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Röntgenstrahlen und der bildgebenden Verfahren (Vol. 194, No. 07, pp. 728-736). Georg Thieme Verlag KG. https://doi.org/ 10.1055/a-1752-0839
Lee, J. Y., Lee, K. S., Seo, B. K., Cho, K. R., Woo, O. H., Song, S. E., ... & Cha, J. (2022). Radiomic machine learning for predicting prognostic biomarkers and molecular subtypes of breast cancer using tumor heterogeneity and angiogenesis properties on MRI. European radiology, 32, 650-660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08146-8
Lin, C. H. A., & Berger, M. S. (2020). Advancing neuro-oncology of glial tumors from big data and multidisciplinary studies. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 146, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03369-8
Nandi, S., Bhaduri, S., Das, D., Ghosh, P., Mandal, M., & Mitra, P. (2024). Deciphering the lexicon of protein targets: a review on multifaceted drug discovery in the era of artificial intelligence. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 21(4), 1563-1590. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c01161
Negut, I., & Bita, B. (2023). Exploring the Potential of Artificial Intelligence for Hydrogel Development—A Short Review. Gels, 9(11), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110845
Parvin, N., Kumar, V., Joo, S. W., & Mandal, T. K. (2024). Cutting-Edge Hydrogel Technologies in Tissue Engineering and Biosensing: An Updated Review. Materials, 17(19), 4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194792
Qing, X., Xu, W., Liu, S., Chen, Z., Ye, C., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Molecular characteristics, clinical significance, and cancer immune interactions of angiogenesis-associated genes in gastric cancer. Frontiers in immunology, 13, 843077. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.843077
Sabir, F., Qindeel, M., Zeeshan, M., Ul Ain, Q., Rahdar, A., Barani, M., ... & Aboudzadeh, M. A. (2021). Onco-receptors targeting in lung cancer via application of surface-modified and hybrid nanoparticles: A cross-disciplinary review. Processes, 9(4), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040621
Saghiri, M. A., Vakhnovetsky, J., & Nadershahi, N. (2022). Scoping review of artificial intelligence and immersive digital tools in dental education. Journal of Dental Education, 86(6), 736-750. https://doi.org/10.1002/jdd.12856
Shen, L., Bai, J., Wang, J., & Shen, B. (2021). The fourth scientific discovery paradigm for precision medicine and healthcare: challenges ahead. Precision Clinical Medicine, 4(2), 80-84. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcmedi/pbab007
Solovchuk, D. R. (2024). Advances in AI-assisted biochip technology for biomedicine. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 177, 116997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116997
Song, C., Xiong, D. D., He, R. Q., Yong, X. Z., Huang, Z. G., Dang, Y. W., ... & Wei, D. M. (2024). Bibliometric study of the application of the chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane model in cancer research: the top 100 most cited articles. Journal of Comparative Pathology, 213, 59-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcpa.2024.07.001
Tu, J. X., Lin, X. T., Ye, H. Q., Yang, S. L., Deng, L. F., Zhu, R. L., ... & Zhang, X. Q. (2022). Global research trends of artificial intelligence applied in esophageal carcinoma: A bibliometric analysis (2000-2022) via CiteSpace and VOSviewer. Frontiers in Oncology, 12, 972357. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.97235
