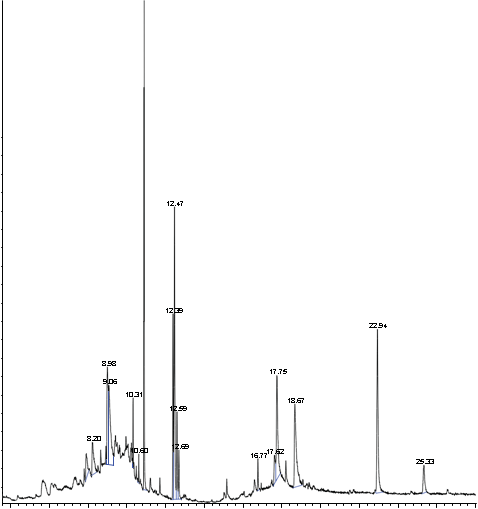
GC-MS Measurement
Mass spectra were obtained using a GC/MS 6890N/5973 Inert (Agilent Technologies). The samples were prepared in GC grade methanol and were injected directly into the ESI source.
Cell culture and Reagents
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), heat inactivated foetal bovine serum (HIFBS), penicillin/streptomycin, and trypsin were obtained from Gibco, Life technology, UK. Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS), sodium chloride, MTT reagent, betulinic acid, suramin, thrombin, fungizone, glutamine, gentamycin, aminocaproic acid and aprotinin were purchased from Sigma – Aldrich, Germany. Fibrinogen was acquired from Calbiochem, USA. All chemicals used in this study were of analytical grade. EAhy 926 cell line was provided by American Type Culture Collection, Rockville, MD, USA.
Plant collection and authentication
Samples of the plant, Crinum Asiaticum (locally known as tembaga suasa) were collected in several places, around Seberang Prai and Balik Pulau, Penang Island. The plant material was sent to the herbarium unit of the School of Biology, USM, for authentication, and a voucher specimen (no. 11537) of the plant (leaves and flowers) was deposited at both the herbarium unit (School of Biology) and herbal room of the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, USM.
Preparation of plant extract
The plant samples were first cut into small pieces, then air-dried followed by heat-dried in the oven, at about 300C, for roughly a week. The dried material was then ground into fine powder, using an electric grinder. They were then subjected to methanol extraction, using a Soxhlet apparatus, to yield the crude extract, which was stored at -20oC until further use.
In vitro anti-angiogenic activity of CALME
EAhy-926 cell proliferation assay
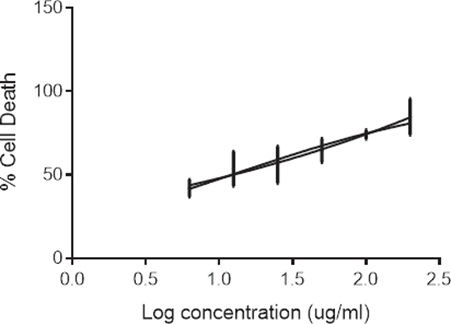
EAhy-926 cells were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 20% of HIFBS, 1% of fungizone, 1% of glutamine, 0.6% of gentamycin and 0.1% of aminocaproic acid. The cells were seeded in 96-well plates, at a density of 2 x 104 cells/well in 100 µl of growth media and kept overnight to facilitate attachment. The cells were exposed to CALME (6.25 to 200 µg/ml) for 48 h. After incubation, the viability of EAhy-926 cells was assessed by MTT (3-4,5 dimethylthiazol-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) assay (Mosmann T.,1983). 20 µl of MTT solution (5 mg/ml in PBS) was added to all wells. After 4-hour incubation at 370C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere, the supernatant (medium or extract) was aspirated from the wells as completely as possible, without disturbing the formazan crystals. A 100 micro-litre volume ofsolvent (DMSO) was then added to each well. After a few minutes at room temperature, to ensure that all crystals were dissolved, the absorbance in each well was measured at 570nm on a multi-well spectrophotometer (ELISA reader).
Migration assay
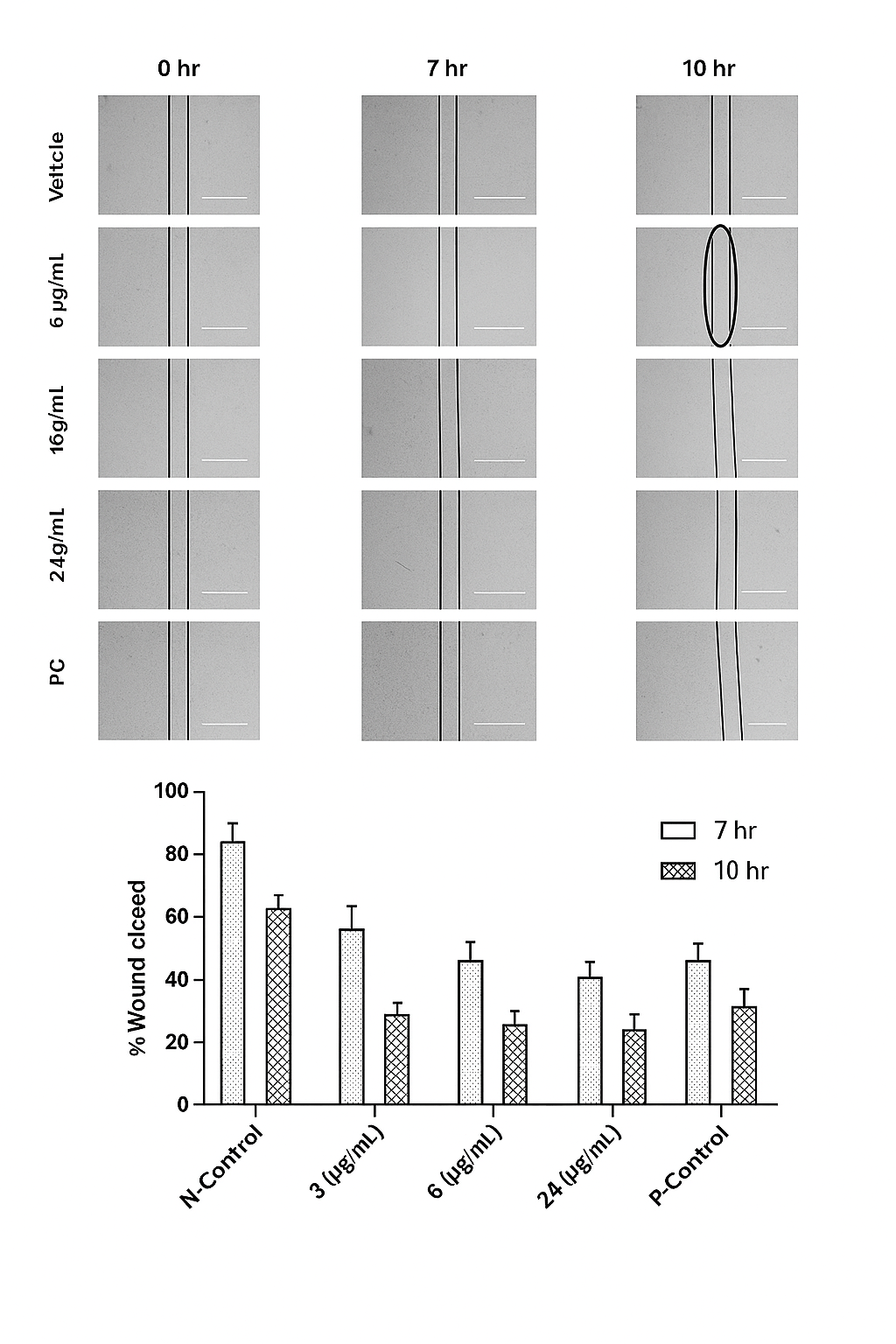
The assay was carried out as described by Liang et al. (2007). Briefly, EAhy-926 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate till the formation of a confluent monolayer, after which a wound was created with 200 µl micropipette tip. The detached cells were removed by washing twice with PBS and the plates were treated with CALME. The wounds were photographed after 7 and 10 h. The width of the cell-free wound was measured under an inverted light microscope equipped with Leica Quin computerized imaging system. 7 fields per well were photographed and a minimum of 7 readings per field were measured.
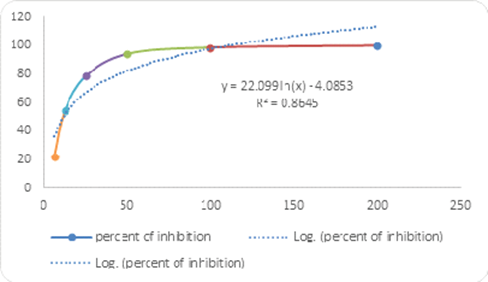
Human VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) inhibition assay
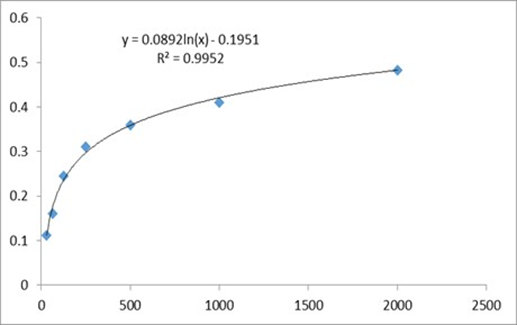
The assay was conducted as per the protocol given in the product (DuoSet® ELISA Development System) information leaflet. Briefly, 60-70% confluent cultures of HUVECs were treated with CALME at 4.15µg/ml (IC50) and 7.47µg/ml (IC90), for 6 h, and cell lysates were prepared using the supplied cell lysis buffer. This assay employs a human VEGF-specific antibody coated on a 96-well plate. Standards and HUVEC lysates were pipetted into the plate so that the VEGF present in the samples would bind the immobilized antibodies. The wells were washed and biotinylated antihuman VEGF antibody was added before the wells were washed again. Then, HRP-conjugated streptavidin was added to the wells. After washing, the colouring agent Tetra Methyl Benzidine substrate solution was pipetted to the wells. The Stop Solution (H2SO4) was added to each well, and the intensity of the colour was measured at 450 nm. At the time of the experiment, a calibration curve of VEGF standard was prepared. The concentration of VEGF in cell lysates was calculated using the log-log regression equation of the best fit line of the standard calibration curve; (y = 0.0892x, R= 0.995). The experiment was repeated two times in triplicates.
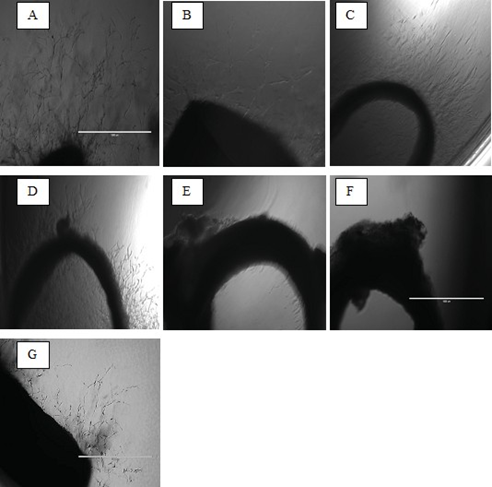
Rat aortic ring assay (ex vivo)
The assay was carried out by utilizing normal, healthy, male Sprague Dawley (Rattus norvegicus) rats of 8-12 weeks old. Sprague Dawley rats are preferred because rats are bigger in size, easily available, easy to handle and the aorta is longer than mice. Male rats are preferable than female ones, to avoid the hormonal disturbance that may occur during the menstrual cycle. The rats were euthanized with 5% CO2 before their aorta excised. The aorta was subsequently cleaned, cut into rings at approximately 1 mm. The rings were placed into a 48-well plate, filled with a special nutrient medium, to which thrombin was added to form the first layer. The extract of different concentrations was then prepared with a second layer of medium. After five days of incubation, the explants were visualized, to study the growth of micro-vessels, which occurred spontaneously at a basal rate, from the cut surfaces of the aortic rings (Nicosia et al., 1992).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis involved use of Graph Pad Prism 5. Data are given as the mean + S.E.M. (standard error mean) and statistics were performed using ANOVA (analysis of variance).