Journal of Primeasia
Impact of Generative AI Models on Neurocybernetics for Enhancing Brain-Computer Interface Adaptability in Motor Disabilities
Poly Rani Ghosh 1*, Shakher Halder 1, Halima Mowla 1
Journal of Primeasia 4 (1) 1-7 https://doi.org/10.25163/primeasia.4140047
Submitted: 10 April 2023 Revised: 17 June 2023 Published: 19 July 2023
Abstract
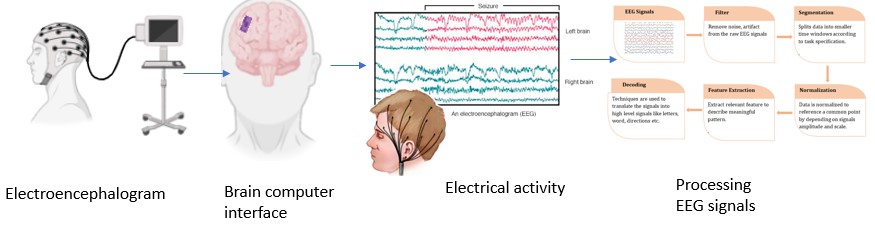
Motor disabilities can arise from conditions such as stroke, spinal cord injuries, or neurodegenerative diseases, severely limiting an individual's movement and communication abilities. Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) represent a promising technology aimed at establishing a direct connection between the brain and external devices, allowing individuals with motor impairments to control assistive technologies using their brain signals. However, conventional BCIs often rely on fixed signal patterns or require extensive user training, presenting challenges for some users and constraining system flexibility. Variability in brain signals and the inability to adapt further impede widespread BCI adoption among this population. This study explores the integration of generative AI models to enhance BCI adaptability for people with motor disabilities. By leveraging generative AI, our framework generates realistic brain signals tailored to each user's specific characteristics. Through rigorous experimentation and case studies, we demonstrate the efficacy of our approach in improving BCI performance and usability. Our findings underscore the transformative potential of generative artificial intelligence in neurocybernetics, illustrating its capacity to advance BCI accessibility and effectiveness in rehabilitating motor disabilities. The limitations of traditional BCIs through innovative AI-driven solutions, this research contributes to the evolving field of assistive technologies. It highlights the pivotal role of generative AI in fostering greater autonomy and quality of life for individuals with motor impairments, paving the way for more inclusive and responsive neurotechnology in the future.
Keywords: Brain-computer interfaces, Motor disabilities, Generative AI, Neurocybernetics, Assistive technologies.
References
Bell, C. J., Shenoy, P., Chalodhorn, R., & Rao, R. P. N. (2008). Control of a humanoid robot by a noninvasive brain-computer interface in humans. Journal of Neural Engineering, 5(2), 214-220. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/5/2/012
Bitbrain Team. (2020, April 23). How deep learning is changing machine learning AI in EEG data processing.
Deng, S., Winter, W., Thorpe, S., & Srinivasan, R. (2011). EEG surface Laplacian using realistic head geometry. International Journal of Bioelectromagnetism, 13(4), 173-177.
Ding, Y., Zhang, C., Cao, M., Wang, Y., Chen, D., & Zhang, N., et al. (2021). Tostagan: An end-to-end two-stage generative adversarial network for brain tumor segmentation. Neurocomputing, 462, 141-153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.066
Fahimi, F., Dosen, S., Ang, K. K., Mrachacz-Kersting, N., & Guan, C. (2020). Generative adversarial networks-based data augmentation for brain–computer interface. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3016666
FMI Staff. (2023, August 30). Exciting advances in brain-computer interfaces and AI.
Generative AI in the enterprise – Model customization. (2024). Published in the USA 03/24 Design Guide H19825.2.
Gill, J. K. (2023, June 29). Large language models (LLMs).
Gill, J. K. (2023, November 21). The complete guide to generative AI architecture.
Gong, C., Jing, C., Chen, X., Pun, C. M., Huang, G., Saha, A., Nieuwoudt, M., Li, H.-X., Hu, Y., & Wang, S. (2023). Generative AI for brain image computing and brain network computing: A review. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 17, 1203104. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1203104
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., & Bengio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 2672-2680).
Guo, J., Wang, C., Wu, Y., Zhang, E., Wang, K., Xu, X., Song, S., Shi, H., & Huang, G. (2024). Zero-shot generative model adaptation via image-specific prompt learning.
Guo, X., & Chen, Y. (2024). Generative AI for synthetic data generation: Methods, challenges and the future. arXiv:2403.04190v1 [cs.LG]
Hochberg, L. R., Serruya, M. D., Friehs, G. M., Mukand, J. A., Saleh, M., Caplan, A. H., Branner, A., Chen, D., Penn, R. D., & Donoghue, J. P. (2006). Neuronal ensemble control of prosthetic devices by a human with tetraplegia. Nature, 442(7099), 164-171. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04970
Hu, S., Lei, B., Wang, S., Wang, Y., Feng, Z., & Shen, Y. (2021). Bidirectional mapping generative adversarial networks for brain MR to PET synthesis. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 41, 145-157. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2021.3107013
Hu, S., Shen, Y., Wang, S., & Lei, B. (2020). Brain MR to PET synthesis via bidirectional generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 698-707). Springer.
Islam, M. R., Rahim, M. A., Akter, H., Kabir, R., & Shin, J. (2018). Optimal IMF selection of EMD for sleep disorder diagnosis using EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applications in Information Technology (pp. 96-101). Aizu-Wakamatsu, Japan.
Jadon, A., & Kumar, S. (2023). Leveraging generative AI models for synthetic data generation in healthcare: Balancing research and privacy. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Applications, Communications and Networking (SmartNets). https://doi.org/10.1109/SmartNets58706.2023.10215825
Jannat, N., Sibli, S. A., Shuhag, M. A. R., & Islam, M. R. (2020). EEG motor signal analysis-based enhanced motor activity recognition using optimal de-noising algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (pp. 125-136). Springer.
Johnson, M. T., Yuan, X., & Ren, Y. (2007). Speech signal enhancement through adaptive wavelet thresholding. Speech Communication, 49(2), 123-133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.specom.2006.12.002
Kingma, D. P., & Welling, M. (2013). Auto-encoding variational Bayes. arXiv:1312.6114v11 [stat.ML]
Lahane, P., Jagtap, J., Inamdar, A., Karne, N., & Dev, R. (2019). A review of recent trends in EEG based brain-computer interface. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Data Science (ICCIDS) (pp. 1-6). Chennai, India.
Lee, S., Jeong, B., Kim, M., Jang, R., Paik, W., Kang, J., et al. (2022). Emergency triage of brain computed tomography via anomaly detection with a deep generative model. Nature Communications, 13, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31808-0
Liu, J., Ji, J., Xun, G., Yao, L., Huai, M., & Zhang, A. (2020). EC-GAN: Inferring brain effective connectivity via generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (pp. 4852-4859). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i04.5921
Luo, Y., Nie, D., Zhan, B., Li, Z., Wu, X., Zhou, J., et al. (2021). Edge-preserving MRI image synthesis via adversarial network with iterative multi-scale fusion. Neurocomputing, 452, 63-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.060
Mo, L., & Wang, S.-Q. (2009). A variational approach to nonlinear two-point boundary value problems. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications, 71, 834-838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2008.12.006
Pan, Y., Liu, M., Lian, C., Xia, Y., & Shen, D. (2019). Disease-image specific generative adversarial network for brain disease diagnosis with incomplete multi-modal neuroimages. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 137-145). Springer.
Pan, Y., Liu, M., Xia, Y., & Shen, D. (2022). Disease-image-specific learning for diagnosis-oriented neuroimage synthesis with incomplete multi-modality data. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 44, 6839-6853. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3091214
Patel, V. L., Shortliffe, E. H., Stefanelli, M., Szolovits, P., Berthold, M. R., Bellazzi, R., & Abu-Hanna, A. (2009). The coming of age of artificial intelligence in medicine. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 46(1), 5-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2008.07.017
Prakash, D. (2024, March 13). Transfer learning in generative AI: A quick guide for developers.
Qiao, C., Hu, X.-Y., Xiao, L., Calhoun, V. D., & Wang, Y.-P. (2021). A deep autoencoder with sparse and graph Laplacian regularization for characterizing dynamic functional connectivity during brain development. Neurocomputing, 456, 97-108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.05.003
Ren, Z., Li, J., Xue, X., Li, X., Yang, F., & Jiao, Z., et al. (2021). Reconstructing seen image from brain activity by visually-guided cognitive representation and adversarial learning. NeuroImage, 228, 117602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117602
Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P., & Ommer, B. (2022). High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 10684-10695).
Rouzrokh, P., Khosravi, B., Faghani, S., Moassefi, M., Vahdati, S., & Erickson, B. J. (2022). Multitask brain tumor inpainting with diffusion models: A methodological report. arXiv:2203.04190v1 [cs.CV]
Sharma, A., & Hamarneh, G. (2019). Missing MRI pulse sequence synthesis using multi-modal generative adversarial network. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 39, 1170-1183. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2945521
Shaw, L., & Routray, A. (2016). Statistical features extraction for multivariate pattern analysis in meditation EEG using PCA. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE EMBS International Student Conference (ISC) (pp. 1-4). Ottawa, ON, Canada.
Shin, H.-C., Ihsani, A., Xu, Z., Mandava, S., Sreenivas, S. T., Forster, C., et al. (2020). Gandalf: Generative adversarial networks with discriminator-adaptive loss fine-tuning for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis from MRI. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 688-697). Springer.
Siebers, P., Janiesch, C., & Zschech, P. (2022). A survey of text representation methods and their genealogy. IEEE Access, 10, 96492-96513.
Song, T.-A., Chowdhury, S. R., Yang, F., & Dutta, J. (2020). PET image super-resolution using generative adversarial networks. Neural Networks, 125, 83-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2020.01.029
Subasi, A., & Gursoy, M. I. (2010). EEG signal classification using PCA, ICA, LDA and support vector machines. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(12), 8659-8666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.06.065
Sundar, L. K. S., Iommi, D., Muzik, O., Chalampalakis, Z., Klebermass, E.-M., Hienert, M., et al. (2021). Conditional generative adversarial networks aided motion correction of dynamic 18F-FDG PET brain studies. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 62, 871-879. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.120.248856
Trotino, G. (2023, August 7). Generative AI synthetic data techniques: Leverage the power.
Upadhyay, U., Sudarshan, V. P., & Awate, S. P. (2021). Uncertainty-aware GAN with adaptive loss for robust MRI image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 3255-3264). Montreal, QC, Canada.
Wang, S., Chen, Z., You, S., Wang, B., Shen, Y., & Lei, B. (2022). Brain stroke lesion segmentation using consistent perception generative adversarial network. Neural Computing and Applications, 34, 8657-8669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06816-8
Wicaksono, K. P., Fujimoto, K., Fushimi, Y., Sakata, A., Okuchi, S., Hinoda, T., et al. (2022). Super-resolution application of generative adversarial network on brain time-of-flight MR angiography: Image quality and diagnostic utility evaluation. European Radiology, 33, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-09103-9
Wolleb, J., Bieder, F., Sandkühler, R., & Cattin, P. C. (2022). Diffusion models for medical anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Singapore.
Wolterink, J. M., Dinkla, A. M., Savenije, M., Seevinck, P. R., van den Berg, C., & Išgum, I. (2017). MR-to-CT synthesis using cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Conference. Long Beach, CA, USA.
Wu, X., Bi, L., Fulham, M., Feng, D. D., Zhou, L., & Kim, J. (2021). Unsupervised brain tumor segmentation using a symmetric-driven adversarial network. Neurocomputing, 455, 242-254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.05.073
Yang, H., Qian, P., & Fan, C. (2020). An indirect multimodal image registration and completion method guided by image synthesis. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2020, 2684851. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2684851
Yang, H., Sun, J., Yang, L., & Xu, Z. (2021). A unified hyper-GAN model for unpaired multi-contrast MR image translation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 127-137). Springer.
Yu, B., Zhou, L., Wang, L., Shi, Y., Fripp, J., & Bourgeat, P. (2019). EA-GANS: Edge-aware generative adversarial networks for cross-modality MR image synthesis. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 38, 1750-1762. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2895894
Yu, W., Lei, B., Ng, M. K., Cheung, A. C., Shen, Y., & Wang, S. (2021a). Tensorizing GAN with high-order pooling for Alzheimer's disease assessment. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems.
Yuan, W., Wei, J., Wang, J., Ma, Q., & Tasdizen, T. (2020). Unified generative adversarial networks for multimodal segmentation from unpaired 3D medical images. Medical Image Analysis, 64, 101731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101731
Zhan, B., Li, D., Wu, X., Zhou, J., & Wang, Y. (2021). Multi-modal MRI image synthesis via GAN with adaption-layer instance normalization. Neurocomputing, 437, 195-206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.01.076
Zhang, L., Wang, L., & Zhu, D. (2020). Recovering brain structural connectivity from functional connectivity via multi-GCN based generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 53-61). Springer.
Zhang, X., Ma, Z., Zheng, H., Li, T., Chen, K., Wang, X., Liu, C., Xu, L., Wu, X., Lin, D., & Lin, H. (2020). The combination of brain-computer interfaces and artificial intelligence: Applications and challenges. Annals of Translational Medicine, 8(11), 712. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.11.109
Zhao, Q., Adeli, E., Honnorat, N., Leng, T., & Pohl, K. M. (2019). Variational autoencoder for regression: Application to brain aging analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 823-831). Springer.
Zhou, B., Wang, R., Chen, M.-K., Mecca, A. P., O'Dell, R. S., Dyck, C. H. V., et al. (2021). Synthesizing multi-tracer PET images for Alzheimer's disease patients using a 3D unified anatomy-aware cyclic adversarial network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 34-43). Springer.
Zuo, Q., Lei, B., Shen, Y., Liu, Y., Feng, Z., & Wang, S. (2021). Multimodal representations learning and adversarial hypergraph fusion for early Alzheimer's disease prediction. In Proceedings of the Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV) (pp. 479-490). Springer.
Recommended articles
Integrating Artificial Intelligence Across the Fashion Value AI Transforming Design, Production, and Consumer Experience
Save
Citation
View
Share
